what are some challenges of using waste biomass for energy
1. What are biomass resources and how can they be utilized for energy production?
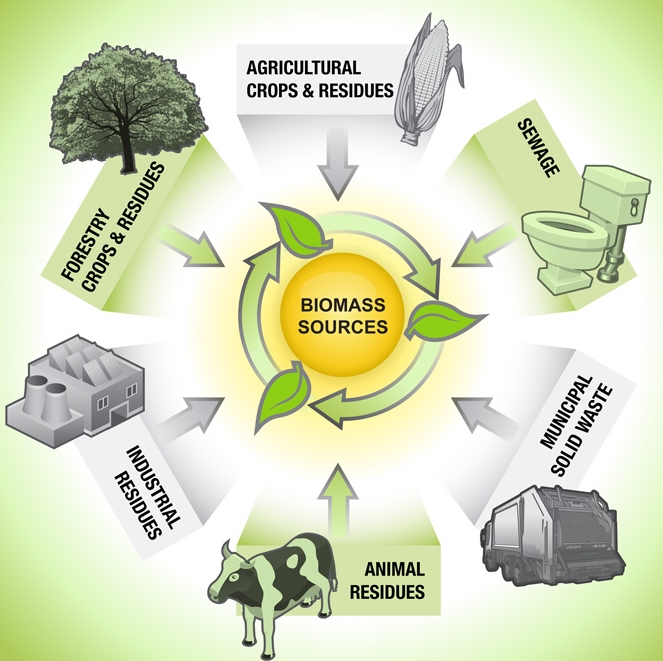
Biomass resources refer to organic materials derived from plants, animals, or waste that can be used to produce energy. These resources include wood, crops, agricultural residues, animal manure, and even municipal solid waste. Biomass can be utilized for energy production through various technologies such as:
- Biomass combustion
- Biogas production
- Biochemical conversion
- Thermal conversion
By harnessing the energy potential of biomass resources, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable and renewable energy future.
2. How does waste-to-energy technology help in converting waste into energy?

Waste-to-energy (WtE) technology plays a crucial role in converting various forms of waste into usable energy. This technology involves the combustion of waste materials, such as municipal solid waste or industrial waste, to generate heat or electricity. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Collection and sorting of waste materials
- Combustion of waste in specialized facilities called waste-to-energy plants
- Heat recovery through boilers or other equipment
- Generation of electricity through steam turbines or engines
Waste-to-energy technology not only helps in reducing the volume of waste going to landfills but also produces renewable energy, contributing to a more sustainable waste management system.
3. What are the benefits of utilizing biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology?
Biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology offer several benefits, including:
- Renewable Energy Generation: By utilizing biomass resources and converting waste into energy, we can reduce our reliance on finite fossil fuel resources and increase the use of clean, renewable energy.
- Waste Management: Biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology provide an efficient solution to managing organic waste, reducing the volume of waste in landfills and minimizing the environmental impact.
- Reduced Emissions: Compared to traditional fossil fuel-based energy generation, biomass and waste-to-energy technologies can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to mitigating climate change.
- Energy Security: Utilizing locally available biomass resources for energy production can enhance energy security by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Overall, biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology offer a sustainable and environmentally beneficial approach to energy production and waste management.
4. How does biomass combustion technology work?
Biomass combustion technology involves the burning of organic materials, such as wood or agricultural waste, to produce heat or electricity. It generally follows these steps:
- Fuel Preparation: Biomass is collected and processed into a suitable form for combustion, such as chips, pellets, or briquettes.
- Combustion: The biomass fuel is ignited in a controlled environment, releasing heat energy through a chemical reaction known as oxidation.
- Heat Recovery: The heat generated from combustion is transferred to a heat exchanger, where it is used to produce hot water, steam, or directly drive turbines for electricity generation.
- Emissions Control: Various measures are implemented to minimize harmful emissions, such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide.
Biomass combustion technology is widely used for heating applications in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, as well as for electricity generation in power plants.
5. How does biogas production from biomass work?
Biogas production from biomass involves the decomposition of organic materials, such as animal manure, food waste, or agricultural residues, in an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment. The process typically includes the following steps:
- Feedstock Preparation: Organic materials are collected and mixed to create a homogeneous feedstock for fermentation.
- Anaerobic Digestion: The feedstock is fed into an anaerobic digester, where bacteria break down the organic matter and produce biogas, mainly composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Gas Treatment: The biogas undergoes purification to remove impurities and moisture, resulting in a cleaner fuel suitable for various applications.
- Biogas Utilization: The purified biogas can be used for electricity generation, heating, cooking, or as a vehicle fuel.
Biogas production from biomass not only generates renewable energy but also offers a sustainable waste management solution by treating organic waste and reducing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
6. What are the main forms of biomass available for energy production?
The main forms of biomass available for energy production include:
- Woody Biomass: This includes trees, branches, wood chips, sawdust, and other wood-based materials. Woody biomass is commonly used for heating, electricity generation, and in the production of biofuels.
- Agricultural Residues: These are byproducts of agricultural activities, such as crop residues (stalks, husks, leaves) and processing residues (straw, bagasse). They can be utilized for energy production through combustion, gasification, or biochemical conversion.
- Energy Crops: Certain crops, such as switchgrass, miscanthus, and willow, are specifically grown for energy purposes. These crops have high biomass yield and can be converted into biofuels or used directly for heat and power production.
- Animal Manure: Livestock waste, such as dung and urine, can be anaerobically digested to produce biogas for energy generation.
- Municipal Solid Waste: Organic components of municipal solid waste can be processed to extract biogas or combusted to produce energy.
Each form of biomass has its own advantages, depending on availability, locality, and specific energy requirements.
7. Are there any challenges or limitations to the utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology?
While biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology offer significant benefits, there are also challenges and limitations associated with their utilization, including:
- Availability and Collection: Biomass resources may not be readily available in all regions, and their collection and transportation can be logistically challenging and costly.
- Economic Viability: The cost of implementing biomass and waste-to-energy projects, including the required infrastructure and technology, can be a significant barrier, particularly for smaller-scale applications.
- Technological Maturity: Some biomass conversion technologies still require further development and optimization to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall performance.
- Emissions and Air Quality: Although biomass and waste-to-energy systems are relatively cleaner than fossil fuel-based alternatives, they still emit certain pollutants which need to be effectively controlled and monitored.
- Competition for Land and Resources: The cultivation of energy crops for biomass production may compete with food crops or other land uses, raising concerns about sustainability and land availability.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes technological advancements, policy support, and sustainable resource management.
8. Can biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology make a significant contribution to renewable energy targets?
Biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology have the potential to make a significant contribution to renewable energy targets. Their advantages, such as wide availability, ability to provide baseload power, and energy conversion versatility, position them as important components in the renewable energy mix. Some key points include:
- Biomass resources, including agricultural residues and energy crops, can be sustainably harvested and replenished, ensuring a continuous supply of feedstock for energy production.
- Waste-to-energy technologies enable the utilization of organic waste streams, reducing landfill usage and associated environmental issues while simultaneously generating energy.
- The energy generated from biomass resources and waste-to-energy conversion can be stored and dispatched as needed, helping to stabilize the grid and provide reliable power supply.
- With proper support, financial incentives, and policy frameworks, biomass and waste-to-energy projects can attract investments and contribute to achieving national and global renewable energy targets.
9. How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources in terms of scalability?
In terms of scalability, biomass resources offer several advantages compared to other renewable energy sources:
- Availability and Reliability: Biomass resources, especially agricultural residues and energy crops, are available in large quantities and can be grown or collected on a continuous basis, providing a reliable and consistent supply for energy production.
- Storage and Dispatchability: Biomass energy can be stored in various forms, such as wood pellets or biogas, allowing for dispatchability and addressing the intermittency challenge often associated with other renewable sources such as wind or solar.
- Flexibility in Conversion Technologies: Biomass can be converted into various forms of energy, including heat, electricity, and transportation fuels, providing flexibility in meeting diverse energy demands.
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: Biomass combustion technologies can be integrated into existing energy infrastructure, repurposing coal-fired power plants or district heating systems to use renewable biomass as a fuel source.
These scalability advantages make biomass resources an attractive option for countries and regions aiming to increase their renewable energy capacity while ensuring grid stability and energy security.
10. How do policies and regulations support the utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology?
Policies and regulations play a crucial role in supporting the utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology. Governments and regulatory bodies implement various measures to promote renewable energy and create a favorable environment for biomass projects, including:
- Feed-In Tariffs: Offering guaranteed payment rates to producers of biomass energy, incentivizing investment and providing revenue predictability.
- Tax Incentives: Providing tax relief or exemptions for companies or individuals engaging in biomass energy projects, making them more financially viable.
- Renewable Portfolio Standards: Requiring utilities or energy suppliers to include a certain percentage of renewable energy, including biomass, in their energy mix, driving demand and supporting market growth.
- Sustainable Biomass Certification: Implementing certification schemes that ensure biomass is sourced sustainably, preventing the use of feedstock from deforestation or causing other environmental harm.
- Research and Development Funding: Allocating funds for research and development activities related to biomass and waste-to-energy technologies, encouraging innovation and technological advancements.
These policies and regulations create a supportive framework that encourages investment, fosters innovation, and promotes the sustainable utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology.
11. Are there any success stories or case studies showcasing the effective utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology?
Yes, there are several success stories and case studies showcasing the effective utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology. Some notable examples include:
- Sweden's District Heating Systems: Sweden has successfully integrated biomass combustion technology into its district heating systems, utilizing wood pellets and other biomass fuels to provide reliable and sustainable heat to residential and commercial buildings.
- Germany's Biogas Industry: Germany has a well-established biogas industry, with numerous biogas plants utilizing agricultural residues, energy crops, and organic waste to produce heat, electricity, and biomethane for various applications.
- United Kingdom's Drax Power Station: The Drax Power Station in the UK has transformed from a coal-fired power plant to a biomass-fired power plant. It now generates a significant portion of the country's renewable electricity by using biomass pellets as a renewable fuel source.
These success stories demonstrate the feasibility, environmental benefits, and potential of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology in real-world applications.
12. How can individuals contribute to the utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology?
Individuals can contribute to the utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology in various ways:
- Support Renewable Energy Policies: Stay informed about renewable energy policies and advocate for their implementation to create a conducive environment for biomass projects.
- Reduce Waste: Practice proper waste management, including recycling and composting, to minimize the amount of organic waste that goes to landfills and maximize the potential for waste-to-energy conversion.
- Explore Residential Biomass Solutions: Evaluate the feasibility of utilizing biomass technologies for heating or electricity generation in residential settings. This can include using wood stoves or boilers, or installing biogas digesters for organic waste treatment.
- Educate Others: Spread awareness about biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology, highlighting their benefits and potential as a sustainable energy solution.
By actively supporting and participating in the utilization of biomass resources and waste-to-energy technology, individuals can contribute to the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.