what form of energy is biomass
Types Of Renewable Power Plants, Solar Power Plant, Biomass Energy
Renewable power plants play a crucial role in meeting our energy needs while minimizing the impact on the environment. In this article, we will explore the different types of renewable power plants, including solar power plants and biomass energy. Let's dive in!
1. What are renewable power plants?
Renewable power plants are installations that generate electricity using renewable sources of energy. These sources are naturally replenished, making them sustainable and environmentally friendly.
An expert explains: Renewable power plants harness the power of natural resources such as sunlight, wind, water, and biomass to generate electricity. By utilizing these inexhaustible sources, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and decrease harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
Key points:
- Renewable power plants generate electricity from renewable sources.
- They contribute to reducing our dependence on fossil fuels.
- Renewable power plants help mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
2. What is a solar power plant?

A solar power plant is a type of renewable power plant that uses solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. These panels consist of photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and generate an electric current.
An expert explains: Solar power plants harness the energy from the sun and convert it into usable electricity. The solar panels capture sunlight, which excites electrons in the photovoltaic cells, creating a flow of electricity. This clean and sustainable source of energy can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities.
Key points:
- Solar power plants convert sunlight into electricity.
- They utilize photovoltaic cells to capture solar energy.
- Solar power is a clean and sustainable source of energy.
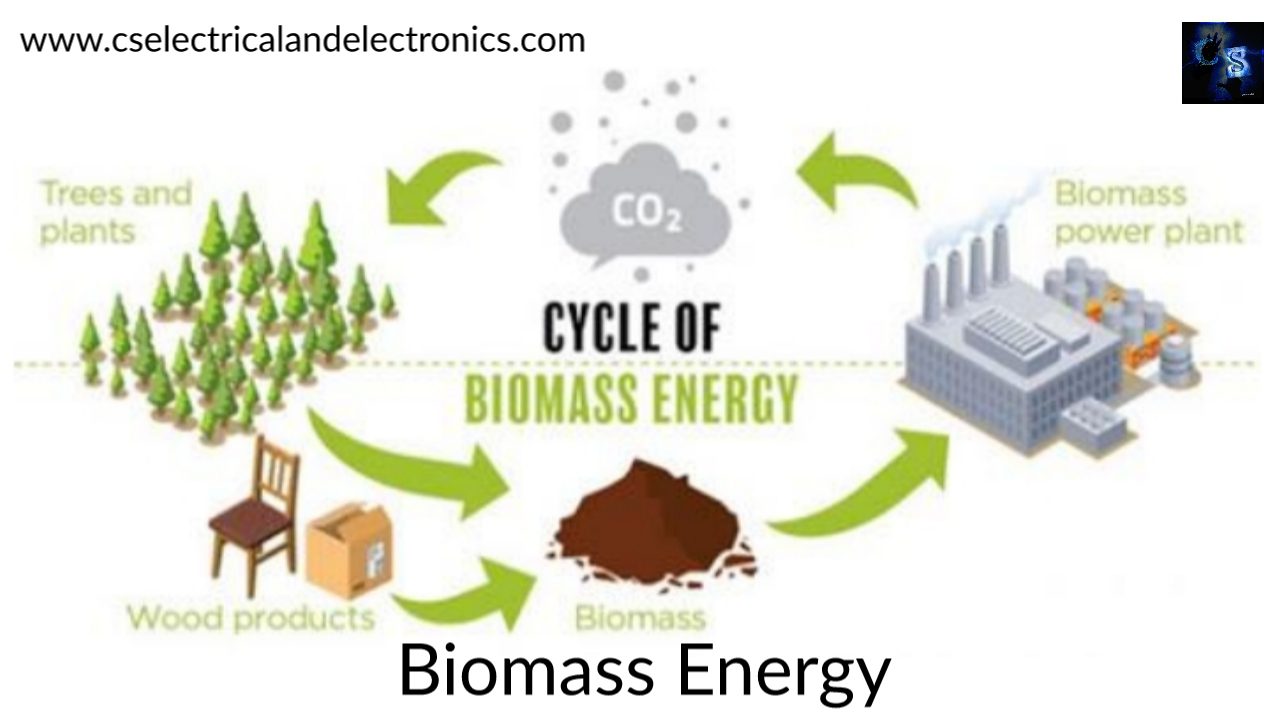
3. What is biomass energy?

Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy derived from organic matter, such as plants and waste materials. It involves using biomass as fuel to generate heat or convert it into electricity.
An expert explains: Biomass energy utilizes organic matter, such as crop residues, wood chips, and even dedicated energy crops, to produce heat or electricity. Through processes like combustion or anaerobic digestion, organic materials are converted into energy-rich biogas or biofuels. This sustainable energy source holds great potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and providing a reliable renewable energy option.
Key points:
- Biomass energy is derived from organic matter.
- It can be used to generate heat or electricity.
- Biomass energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Pros and Cons of Renewable Energy You May Not Know About
Renewable energy offers numerous advantages in our journey towards a sustainable future. However, it's essential to consider both the benefits and drawbacks. Let's explore some of the pros and cons of renewable energy.
4. What are the advantages of renewable energy?

Renewable energy has several advantages that make it an attractive alternative to conventional energy sources. Some benefits include:
An expert explains:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, helping combat climate change.
- Energy availability: Renewable sources are abundant and available in various forms, ensuring a reliable energy supply in the long run.
- Energy independence: By relying on renewable energy, countries can reduce dependence on foreign oil imports and enhance energy security.
- Job creation: The renewable energy industry creates numerous job opportunities, contributing to economic growth and sustainability.
5. What are the challenges of renewable energy?

While renewable energy brings many benefits, it also faces certain challenges and limitations. It's important to understand the potential drawbacks, which include:
An expert explains:
- Intermittency: Some renewable sources, like solar and wind, rely on weather conditions, leading to intermittent energy generation.
- High initial costs: The upfront costs of installing renewable energy systems can be higher compared to conventional energy infrastructure.
- Location limitations: Certain renewable sources may require specific geographic conditions, limiting their widespread implementation.
- Energy storage: Storing excess energy for future use remains a significant challenge in the renewable energy sector.
6. How does renewable energy help reduce carbon emissions?

Renewable energy plays a crucial role in mitigating carbon emissions, contributing to global efforts in combating climate change. Here's how it helps:
An expert explains:
- Replacing fossil fuels: Renewable energy sources replace traditional fossil fuels, which release large amounts of carbon dioxide when burned for energy.
- Zero emissions: Many renewable sources, such as solar and wind, produce electricity without any carbon emissions, reducing the carbon footprint.
- Energy efficiency: Renewable energy technologies are becoming increasingly efficient, allowing for greater energy output with reduced emissions.
- System integration: Combining various renewable energy sources can create a more balanced and reliable carbon-neutral energy system.
7. Are there any government incentives for renewable energy adoption?

Governments worldwide recognize the importance of renewable energy and often provide incentives to promote its adoption. These incentives can include:
An expert explains:
- Financial incentives: Governments may offer tax credits, grants, or subsidies to individuals or businesses investing in renewable energy systems.
- Feed-in tariffs: Some countries guarantee a fixed payment rate for renewable energy producers, creating a stable income stream.
- Renewable portfolio standards: Governments set a minimum renewable energy target, compelling utilities to generate or purchase a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources.
- Green certificates: Renewable energy producers can earn tradable certificates for each unit of electricity they generate, providing additional revenue streams.
8. How do solar power plants work during times of low sunlight?

Solar power plants depend on sunlight to generate electricity, but what happens during periods of low sunlight? Here's how they continue functioning:
An expert explains:
- Storage systems: Some solar power plants incorporate energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store excess electricity generated during peak sunlight hours. This stored energy can be utilized when sunlight is scarce.
- Grid integration: Solar power plants connected to the electrical grid can draw power from the grid during low sunlight periods or when demand exceeds solar generation capabilities.
- Complementary energy sources: In certain cases, solar power plants may be coupled with other renewable sources, like wind or hydro, to maintain consistent electricity generation throughout the day.
9. Can biomass energy be used for heating purposes?

Biomass energy is versatile and can indeed be used for heating purposes. Here's how biomass generates heat:
An expert explains:
- Combustion: Biomass materials, such as wood or agricultural residues, can be burned in specially designed boilers or furnaces to produce heat. This heat can be used for space heating, water heating, or in industrial processes.
- Biomass pellets: Biomass can also be processed into pellets, which offer consistent heating values and can be easily utilized in residential or commercial heating systems.
- Community heating systems: Biomass energy can be utilized in district heating systems, where a centralized plant generates heat for a whole community or district using biomass as fuel.
10. Are there any environmental concerns associated with biomass energy?

While biomass energy is considered renewable, there are some environmental concerns that need to be addressed. Here are a few:
An expert explains:
- Air pollution: The combustion of biomass materials can release pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. Proper emission controls and sustainable harvesting practices can help mitigate these impacts.
- Land usage: Cultivating dedicated energy crops for biomass production may require land that could otherwise be used for food crops or natural ecosystems. Sustainable land management practices are necessary to minimize adverse effects.
- Transportation emissions: Biomass fuels often need to be transported from the production site to the power plant, resulting in carbon emissions. Localized sourcing or optimizing transportation methods can help reduce this impact.
11. How can individuals contribute to renewable energy adoption?

Individuals can play a crucial role in driving renewable energy adoption. Here's how they can contribute:
An expert explains:
- Install rooftop solar panels: Homeowners can invest in solar panels to generate their own clean electricity, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources.
- Support renewable energy suppliers: Individuals can choose to purchase electricity from renewable energy suppliers, encouraging the growth of the renewable energy market.
- Practice energy efficiency: Conserving energy through simple measures like turning off lights, using energy-efficient appliances, and insulating homes can significantly reduce overall energy demand.
- Advocate for renewable energy policies: Engaging with local communities and policymakers to advocate for renewable energy incentives and regulations can help accelerate the transition to cleaner energy sources.
12. What does the future hold for renewable power plants?

The future of renewable power plants looks promising, with several advancements and trends shaping the industry. Here's a glimpse into what lies ahead:
An expert explains:
- Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development are continually improving the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy technologies, making them more economically viable.
- Energy storage breakthroughs: Advances in energy storage technologies are essential for overcoming the intermittency of renewable sources and ensuring a stable power supply.
- Smart grid integration: Enhanced grid management and intelligent energy distribution systems will enable seamless integration of renewable power plants, maximizing their potential and optimizing energy flows.
- Industry collaboration: Increasing collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities will facilitate the transition to renewable energy by fostering innovation, sharing best practices, and driving investment.
As we explore and embrace renewable power plants, we take significant steps towards a sustainable and greener future. By harnessing the power of renewable sources, we can create a world powered by clean energy and mitigate the impacts of climate change.